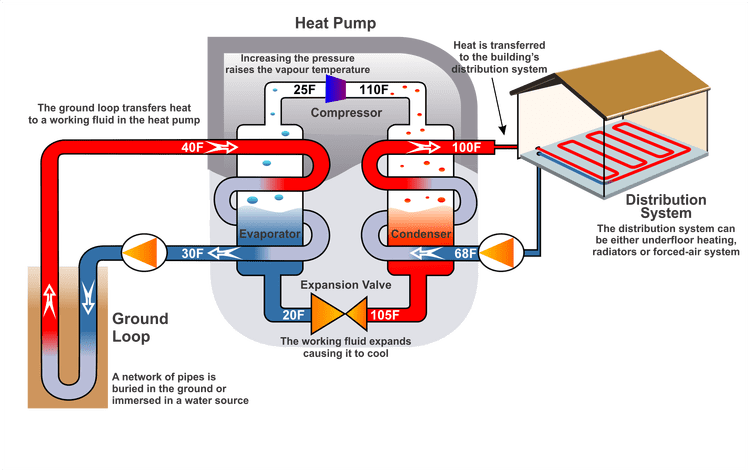
A heat pump is a thermodynamic system that takes away the energy of one medium (usually a lower level), is passed on to another medium.
The very name of the “pump” speaks enough about what it actually is doing. Like any other, the heat pump raises the level. The water pump raises the water level at the expense of the energy consumed, and the heat pump raises the energy level at the expense of the energy taken from the other medium (usually water, air or soil). Heating with heat pumps can save up to 75% in relation to other types of heating.
The advantages of using a heat pump are as follows:
• Use renewable energy (geothermal energy is included in renewable energy sources),
• Use only 20-25% of electricity for your work,
• Does not require the use of a chimney (about 30% of the energy produced in the boiler on solid fuel, goes through a chimney),
• Automated operation
• Does not require any maintenance,
• There is no need to buy energy in advance,
• The ability to program work during a lower tariff,
• No open flame (no possibility of causing fire).
The room is heated by radiators, ventilation fans (fancoils) or underfloor heating. The highest savings are achieved by combining the heat pump and underfloor heating, as with the lowering of the temperature in the system, the heating coefficient increases significantly, and it is known that underfloor heating requires lower temperatures than the radiator.
On the other hand, the fan coil is a good solution because the proctor is possible and heated and cooled, which is not the case in floor and radiator heating.
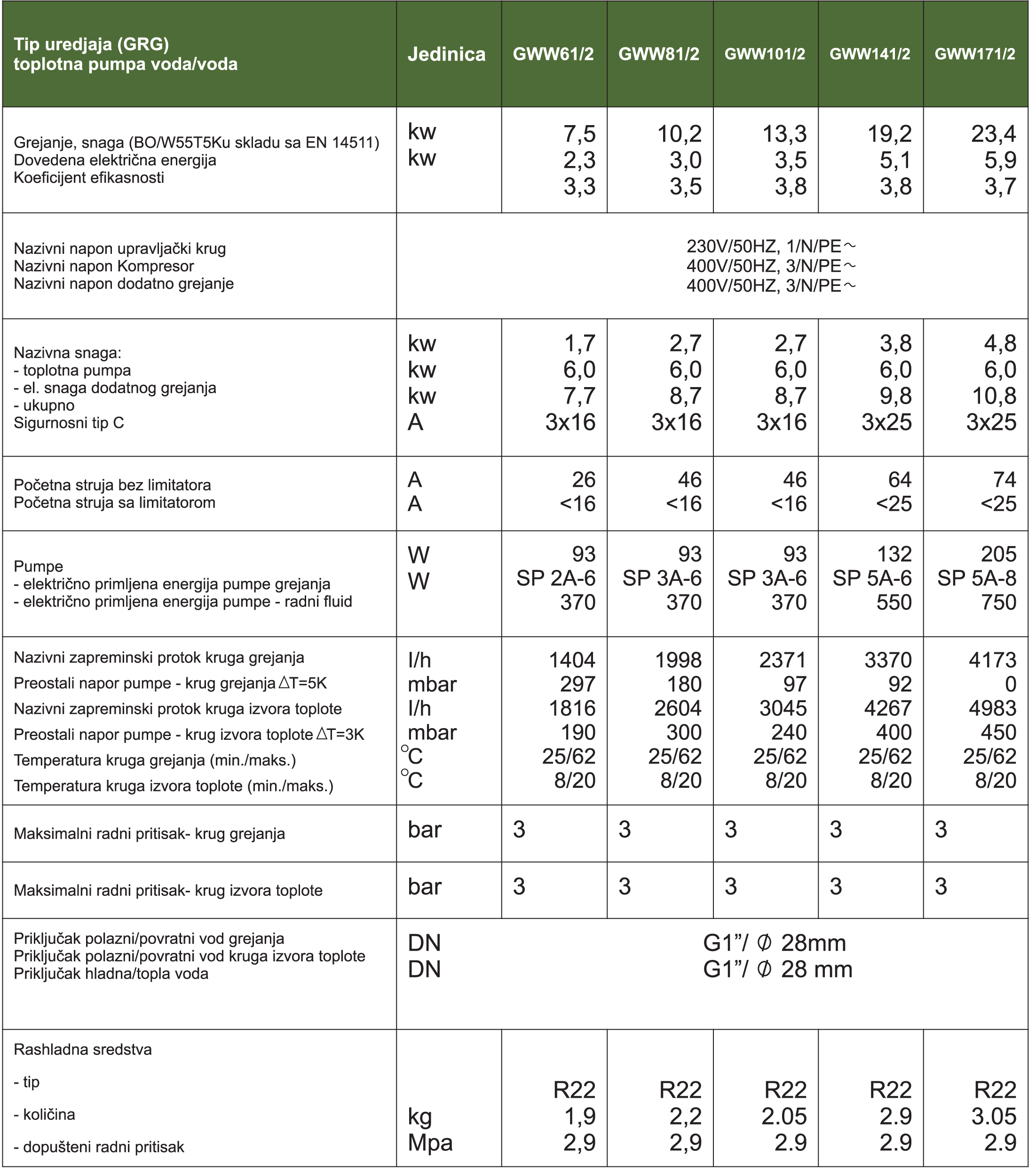
For the user it is most important to know that using a heat pump for heating space and sanitary water can achieve significant savings.